Diagnosis is important to detect or diagnose breast cancer and to decide upon further treatment. There are various techniques and tests that can be used to diagnose breast cancer. These include Clinical Breast Examination (CBE), Mammography, Ultrasound, Automated Breast Volume Scanner (ABVS), Biopsy and several diagnostic laboratory tests.
Breast Self- Examination (BSE)
Breast Self-examination is the best method for Early detection of breast cancer.
Breast Self- Examination (BSE) is how you check yourself for suspicious lumps or thickening. BSE should be conducted every month, 4 or 5 days after your periods. If you have achieved menopause, you should choose one day of the month to maintain regular breast examination.
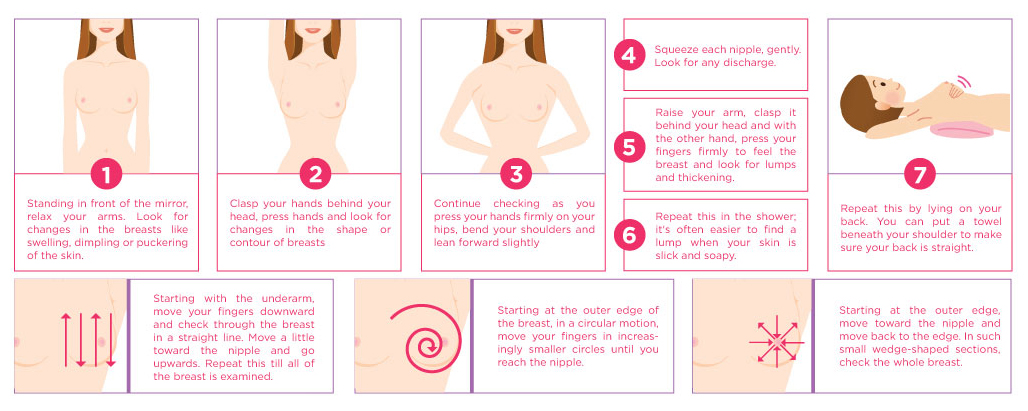
This is one of the key methods of breast cancer detection. In the 2003 National Health Interview Survey (NHIS), about 57% of the 361 breast cancer female survivors (diagnosed between 1980 and 2003) reported a self-detection method of breast cancer (either by purposeful examination or by accident).
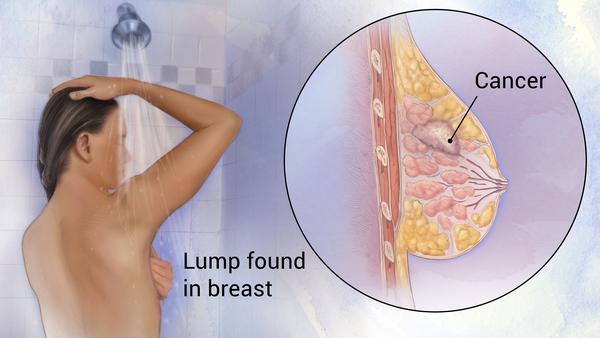
CBE should be done every year for women over 30 years of age and once every three years for women in their 20’s.
Mammography should be done every year for women over 40 years of age. It is a technique that uses X-rays to produce images of the breasts for examination and diagnosis. This procedure can detect early, pre-cancerous lesions.
Ultrasound is an imaging technique that produces images of the breasts on a viewing screen and is used to determine the type of abnormality detected by mammography or CBE.
ABVS is a technique that produces a 3D image of the breast and is used to detect tumours in women with dense breasts (as is the case with Indian women). Biopsy involves removing a tissue sample from the affected breast for further analysis using a needle. There are different types of biopsies such as FNAC, Trucut biopsy, Vacuum Assisted Biopsy (VAB) and robotic stereotactic biopsy. Biopsy is considered only when suspicious lesions are detected by mammography or ultrasound, and is a scarless and painless procedure. Laboratory tests such as hormone receptor status, ER/PR/HER2 status, FISH are conducted to detect the type of tumour and to determine the extent to which it has spread.
Prevention of Breast Cancer
However, high the risk of breast cancer must not scare you; it does not necessarily mean you will develop breast cancer.
You can just follow these simple steps to reduce the risk caused by modifiable risk factors:
- Adapt your lifestyle to include exercising in your daily routine. A stretch in time saves lives!
- Avoid fast food and follow a healthy diet, rich in fruits and vegetables. An apple a day, keeps the doctor away!
- Give up on harmful habits such as consuming alcohol and smoking cigarettes. Bad habits die hard, but it’s better to lose them than hurting your breasts.
- Go for annual health check-ups, including screening of common cancers by your doctor.
Remember that old saying? Health is Wealth! Although genetic predisposition is a non-modifiable risk factor and nothing much can be done to prevent its risk, it is very important that you get counselled about it Genetic counselling will allow you to understand the risks of this disease, its diagnosis by various genetic tests, the further procedure as advised by the doctor, and your management and family planning options. It is very crucial for you to be genetically counselled because this can help you and your family make informed decisions about genetic testing for mutations (like BRCA1 and BRCA2), and can assess the risk of you having the disease. It can also help you in planning your pregnancy.
There is no need to shy away from genetic counselling. It’s better to do it now than regret later. At Orchids, we have a dedicated Risk Reduction Clinic to identify, counsel and manage women at high risk by providing closer surveillance for better prognosis and outcomes.
